Global Salary Levels and Average Income: A Comparative Overview
In a world marked by economic disparity and varied living standards across nations, salary levels and average income are crucial indicators reflecting a country's economic and social health. Wage differences don't arise in a vacuum; they are shaped by multiple factors. These include the strength of the national economy, productivity levels, the development of industrial and service sectors, the cost of living, and government policies on taxes and minimum wages. In countries with robust economies and advanced infrastructure, such as the United States, Switzerland, and Norway, salaries are relatively high to match elevated living expenses. Conversely, in developing nations with slower economic growth and weaker local production, average incomes are significantly lower, leading to clear disparities in social welfare.
Understanding Salary Levels and Average Income
Salary levels and average income are vital economic indicators used to measure the living and economic conditions of individuals within a country. Average income refers to the typical amount an individual earns over a specific period, such as a month or year. It is calculated by summing all wages for workers and dividing by their total number, providing a general picture of individual earnings in a society. Salary levels relate to a country's ability to ensure sufficient income for its workers, enabling them to meet basic needs and achieve a decent quality of life. This level is influenced by economic growth, inflation rates, the cost of living, productivity, and government wage and tax policies. Studying these indicators helps us understand economic differences between nations and assess income distribution fairness within a society.
Key Factors Influencing Global Salary Levels
National Economic Strength
A nation's economy significantly impacts its internal salary levels. A strong and diverse economy generally leads to more job opportunities and higher wages, thanks to flourishing productive, commercial, and service sectors. In major industrialized nations like the United States, Germany, and Japan, sustained economic growth increases demand for skilled labor, raising overall average wages. Conversely, countries with weak economies, or those overly reliant on a single sector, often face limited economic opportunities, resulting in lower salaries and reduced purchasing power for citizens.
Education and Specialized Skills
Education and vocational training play a pivotal role in determining individual income. The higher an individual's education and specialized skills, the greater their value in the labor market, leading to higher pay. Countries that invest in their educational systems and encourage continuous training foster a competitive work environment based on competence and experience, which positively reflects on salaries. For instance, Scandinavian countries, known for their strong emphasis on technical and vocational education, are among the nations with the highest global wages.
Cost of Living
The cost of living is a fundamental factor directly linked to salary levels. In countries with high prices for housing, food, and services, wages tend to rise to match these expenses. However, high salaries do not automatically guarantee a comfortable life; daily expenses can consume most of the income, as seen in countries like Switzerland and Norway, where the cost of living is among the highest worldwide. Therefore, salaries must always be considered within their broader economic and social context, not in isolation.
Government Policies
Government policies are crucial in shaping salary levels through labor market regulations, such as setting minimum wages, tax laws, and social security systems. Governments that adopt fair policies and support equitable income distribution contribute to improving living standards and reducing social disparities. Conversely, a lack of oversight or weak regulations can lead to significant wage gaps and exploitation of certain worker groups. State intervention is thus critical to ensuring labor market balance and national economic stability.
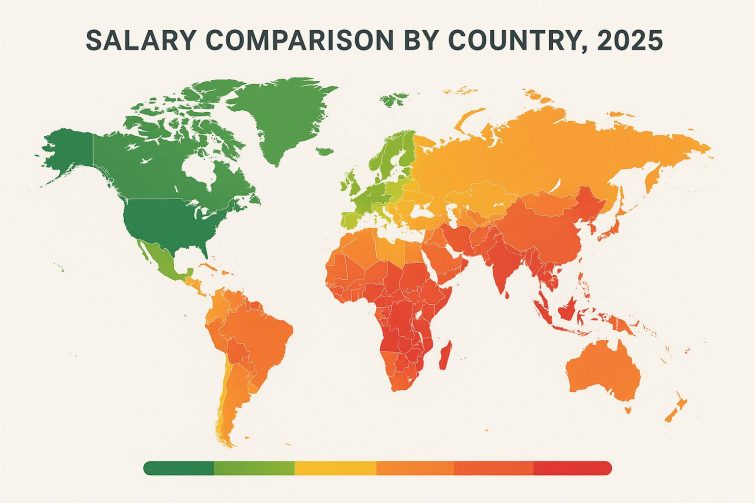
Global Overview: Countries by Average Salary
Top-Paying Nations
Several countries consistently rank highest in terms of average salaries globally.
- Switzerland: Switzerland boasts some of the highest average wages worldwide, with individual incomes often exceeding $7,000 per month. This is attributed to its strong economy, stable financial system, and advanced sectors like banking, technology, and pharmaceuticals. Given the exceptionally high cost of living in Switzerland, these elevated salaries are essential to cover daily expenses for housing, services, and education.
- United States: The United States features high average salaries, around $6,000 per month, though this varies significantly by state depending on the cost of living and economic activity. Major states like California and New York offer higher wages due to robust technology and financial sectors. The American market also provides extensive career advancement opportunities, making it an attractive destination for skilled professionals globally.
- Luxembourg and Norway: Luxembourg and Norway are also among the top-paying countries, with salaries ranging from $5,000 to $6,500 per month. Luxembourg is a global financial hub attracting major corporations, while Norway's strong economy is based on oil and gas, complemented by an advanced social welfare system that ensures equitable wealth distribution. Both economic stability and social policies contribute to high wage levels and improved quality of life.
- Australia and Canada: Australia and Canada offer relatively high salaries, averaging between $4,500 and $6,000 per month, alongside a stable living environment and balanced social systems. Both nations benefit from diverse economies encompassing agriculture, industry, services, and energy. They prioritize citizen welfare and provide high-quality education and healthcare services. This balance of income and quality of life makes them highly appealing to immigrants and skilled workers.
Middle-Income Nations
Several countries fall into the medium-income bracket, offering moderate salaries.
- Spain and Portugal: Spain and Portugal are classified as medium-income countries, with average wages between $2,000 and $2,500 per month. Their economies heavily rely on tourism, services, and small to medium-sized enterprises. Despite lower salaries compared to Western European counterparts, the moderate cost of living allows for a relatively acceptable standard of living. Both nations are actively working to stimulate economic growth and create job opportunities, particularly in technology and renewable energy.
- Eastern European Countries (Poland and Czech Republic): Poland and the Czech Republic are prominent Eastern European countries experiencing stable economic growth, with average wages ranging from $1,500 to $2,000 per month. Their accession to the European Union has boosted foreign investment and infrastructure development, positively impacting their labor markets. These countries are also focused on improving education and vocational training to enhance workforce efficiency, paving the way for gradual wage increases in the coming years.
- Latin American Countries (Chile and Mexico): Nations like Chile and Mexico are categorized as medium-income in Latin America, with average earnings between $1,200 and $2,000 per month. Despite regional economic challenges, these countries are seeing gradual improvements in wage levels due to economic reforms and increased investments in industrial, technological, and service sectors. Governments are also working to reduce social disparities and improve working conditions through policies aimed at achieving fair income distribution.
Lower-Income Nations
Conversely, some regions struggle with significantly lower average salaries.
- Sub-Saharan Africa (Nigeria and Ethiopia): Sub-Saharan African countries, such as Nigeria and Ethiopia, have some of the lowest average wages globally, with incomes often not exceeding $400 per month. This low level is linked to several factors, including weak infrastructure, limited industrial job opportunities, and most populations relying on traditional agriculture for income. Political instability, high poverty rates, and a lack of foreign investment further hinder economic growth, directly impacting salary and living standards.
- Some Asian Countries (Bangladesh and Nepal): Certain Asian countries, including Bangladesh and Nepal, are classified among the lowest-paying globally, with average incomes of only a few hundred dollars per month. Their economies depend on light industries like textiles and agriculture, where cheap labor attracts foreign investment. However, low wages are often accompanied by poor basic services and high rates of unemployment and poverty. In recent years, these countries have been working to improve economic policies, education, and infrastructure to raise income levels and enhance the quality of life for their citizens.
Salaries in the Arab World
The Arab world presents a varied picture regarding salary levels.
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries: The GCC countries lead in salary levels, thanks to their strong oil-based economies.
- UAE, Qatar, and Kuwait: Average salaries range between $3,000 and $5,000 per month.
- Saudi Arabia: Salaries typically fall between $2,500 and $4,000, depending on the profession.
- Medium-Income Arab Countries:
- Jordan, Morocco, and Tunisia: Average wages range from $600 to $1,200 per month.
- Egypt and Algeria: Salaries average less than $500 per month, but are gradually improving with local economic advancements.
Beyond the Numbers: Average Salary vs. Purchasing Power
A high salary in some countries doesn't automatically translate to a luxurious lifestyle. The true measure is purchasing power—the amount an individual can buy with their income. For example, $3,000 per month in Switzerland might barely cover housing and food expenses, whereas the same amount could provide a very comfortable life in another country. It is essential to consider the local cost of living when evaluating salary levels.
Technology's Impact on Salaries and the Digital Divide
The evolution of technology and digital transformation has profoundly impacted global salary levels. Technological innovations and the rise of the digital economy have created new jobs demanding advanced skills in areas like programming, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. These roles command relatively high wages compared to traditional occupations. Conversely, countries unable to adapt to this digital shift or invest in technological infrastructure and specialized education often lag in job opportunities and wages. This widens the economic gap between developed and developing nations.
The increasing global demand for digital talent makes highly skilled professionals invaluable assets to companies, leading to significant salary increases for them, while wages for traditional roles continue to decline. Thus, digital transformation not only alters the nature of work but also drives global wage disparities, linking economic innovation to higher income potential. Investing in technological education and vocational training is therefore imperative for any nation seeking to raise its citizens' income levels and keep pace with the modern economy.
Strategies to Boost Income in Developing Countries
Improving income levels in developing countries requires a multifaceted approach:
- Invest in education and vocational training.
- Encourage entrepreneurship and support small businesses.
- Improve working conditions and raise the minimum wage.
- Promote tax fairness to ensure more balanced income distribution.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the classification of countries by global salary levels and average income reflects their economic and social progress. Nations that invest in their people, education, and technology generally see an improvement in quality of life and wage levels. While rapid economic changes mean the gap between rich and poor countries remains significant, it is not insurmountable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between average wage and individual income?
Average wage typically refers only to employed individuals, whereas individual income includes all citizens, even those not working.
Do higher salaries always guarantee a better life?
Not necessarily, as the cost of living can be very high in some countries, offsetting the higher income.
Which Arab countries are most attractive for employment in terms of salaries?
The UAE, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia generally top the list for higher wages and opportunities.
How does technology affect average wages?
Technology increases the demand for technical skills, which in turn raises the wages for professionals in these specialized fields.
What is the future outlook for wages in the Arab world?
Wages are expected to improve gradually with economic diversification and the expansion of sectors such as technology and renewable energy.
0 comments:
Post a Comment